Working With Date and Time Information
Storage of Time/Date Values
Datameer X stores and calculates dates as UNIX Time and uses the 1900 date system. Dates are converted into milliseconds (returning the difference between the current time and midnight, January 1, 1970 UTC).
Example
| Date | Unix Time Conversion |
|---|---|
| Jan 1,1970 00:00:01 | 1 |
| Jan 1,2016 00:00:01 | 1451606401 |
Constants
A constant is an identifier whose associated value cannot typically be altered by the program during its execution.
| Constant | Component |
|---|---|
| ms | milliseconds |
| s | seconds |
| m | minutes |
| h | hours |
| d | days |
These time constants can be used when building formulas and functions as well as when using filters in order to manipulate time/date data.
Examples of time/date constants
Example of Date/Time constants within functions
*Today is October 10, 2012
| Function(s) | Result | Function with constant | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| TODAY() | Oct 10, 2012 12:00:00 AM | TODAY()-5h | Oct 09, 2012 07:00:00 PM |
| TODAY() | Oct 10, 2012 12:00:00 AM | TODAY()+8h+5m | Oct 10, 2012 08:05:00 AM |
| TIMESTAMP() | 1,349,820,000,000 | TIMESTAMP()+2d | 1,349,992,800,000 |
| TIMESTAMP() | 1,349,820,000,000 | TIMESTAMP()+45d+12h | 1,353,751,200,000 |
Example of Date/Time constant within a filter
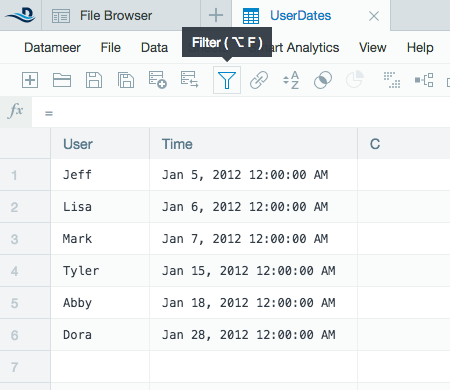
Original data:
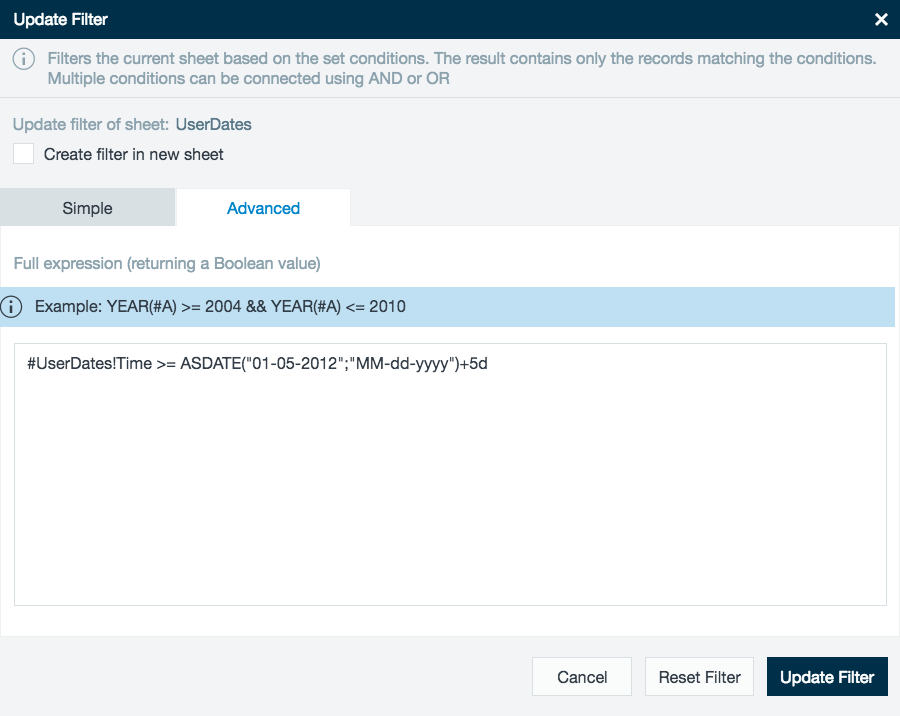
- Apply a filter and choose Advanced.
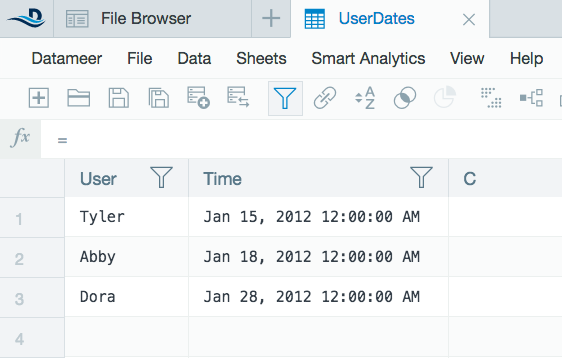
- Type in the filter you want to apply including time constant if needed. For example, #UserDates!Time >= ASDATE("01-05-2012";"MM-dd-yyyy")+5d.
- View the data on the filtered sheet.
Example of Date/Time constant within a formula
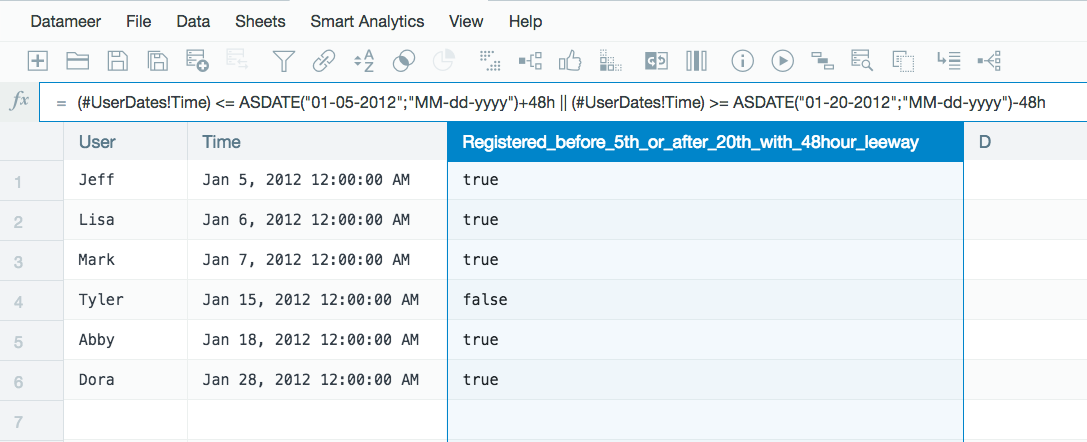
Original data:
- Open a calculation workbook sheet and create your formula, for example: (#UserDates!Time) <= ASDATE("01-05-2012";"MM-dd-yyyy")+48h || (#UserDates!Time) >= ASDATE("01-20-2012";"MM-dd-yyyy")-48h.
- View the formula results.
Modifying Date/Time
Modify values with a data date type using the ADDTODATE function. This function allows for both adding and subtracting from dates and times and takes daylights savings time and leap years into account.
Operators (+/-) outside the ADDTODATE function aren't supported.